Picture this: You’ve spent years building your dream business. Maybe it’s a cozy neighborhood café, a small law firm, or a tech startup with a team of passionate folks. Things are finally running smoothly. And then disaster strikes.
It could be a fire, a flood, or even a cyberattack. Your operations grind to a halt. No customers. No income. But the rent still needs to be paid, employee salaries are due, and bills keep piling up.
That’s where Business Interruption Insurance steps in and trust me, it can be a lifeline when you need it most.
In this post, I’m going to walk you through everything you need to know about Business Interruption Insurance in the U.S. in plain English. Whether you’re just starting out or have been in business for decades, this coverage could be the difference between closing your doors for good or bouncing back stronger.
What Is Business Interruption Insurance?
Business Interruption Insurance (sometimes called business income insurance) helps cover lost income and operational expenses when your business is forced to shut down due to a covered event like fire, natural disasters, or other physical damage.
Let’s say you run a family-owned pizzeria in downtown Atlanta. One night, a fire in the kitchen damages your equipment and building. While your property insurance may pay for repairs, what about the weeks or months your shop stays closed? That’s where business interruption coverage kicks in it helps replace your lost revenue during the downtime.
Let’s get into the real meat of the matter: What does business interruption insurance actually cover? Because let’s face it insurance jargon can be overwhelming. And the last thing you want is to assume you’re protected… only to find out you’re not when disaster hits.
I’ve learned (sometimes the hard way) that reading the fine print and truly understanding your policy is just as important as having one.
So let’s break it down no fluff, no confusing language. Just real talk.
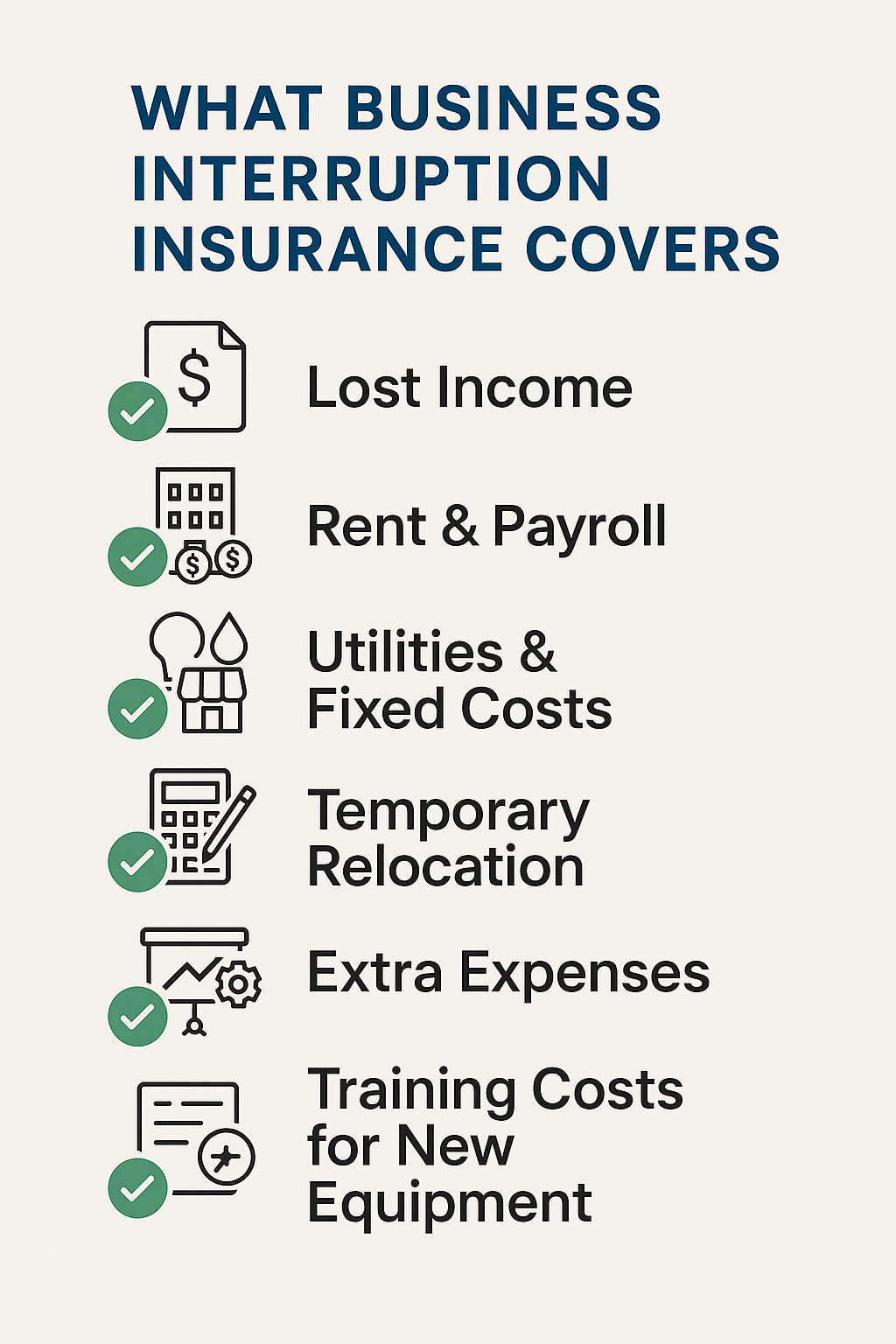
It typically covers:
Lost Income: The Heart of the Coverage
This is the big one.
At its core, business interruption insurance is designed to reimburse your business for the income you would have earned during the period you’re forced to shut down.
Let’s say your photography studio brings in $10,000 a month, and a fire forces you to close for two months. Based on your previous financial records, your policy may cover that lost revenue as if your business had never skipped a beat.
But here’s the catch: the amount you receive is tied to your past financial performance. So keeping accurate, up-to-date books isn’t just smart business it’s essential for getting paid fairly when filing a claim.
Pro tip: If your revenue fluctuates seasonally (like a tax preparation service), make sure your policy accounts for that. Otherwise, you might come up short when it matters most.
Fixed Operating Expenses: Bills Don’t Take a Break
Your business might be closed, but your bills? Oh, they’re still showing up on time.
Thankfully, business interruption insurance can help cover fixed operating costs you’re still responsible for, such as:
- Rent or mortgage payments
- Utilities
- Property taxes
- Equipment leases
- Employee wages
This is HUGE, especially if you’re committed to keeping your team intact during the downtime.
I once spoke to a boutique owner in Minneapolis who said her business interruption policy literally “kept the lights on” while her shop was being renovated after a ceiling leak. She was able to pay her employees and retain her loyal manager something that made reopening much smoother.
Temporary Relocation Costs
Sometimes, getting back to business means moving your operations elsewhere at least temporarily. Maybe your office is undergoing repairs, or your storefront is off-limits due to structural damage.
In those cases, your policy may help cover relocation expenses, including:
- Renting a temporary office or storefront
- Moving equipment or inventory
- Marketing costs to inform customers of your new location
Imagine you run a dog grooming business. Your space is damaged in a minor fire, but you’re able to rent a mobile grooming van and operate in parking lots or driveways for a few weeks. If your policy includes this type of coverage, it might help pay for the van rental and marketing to get the word out.
It’s not just about surviving it’s about adapting fast.
Training for New Equipment
Let’s say your business uses specialized equipment maybe a commercial espresso machine, a CNC router, or even a POS system. If that equipment needs to be replaced after a covered loss, your staff might need training to use the new version.
Many business interruption policies will help pay for that training period, so your team isn’t thrown into the deep end.
It’s a detail that’s easy to overlook but it can make a big difference in how quickly and confidently your business can get back on its feet.
Extra Expenses: The Unexpected Boost
This is one of my favorite parts of a good business interruption policy extra expense coverage.
This part covers any reasonable, necessary expenses you wouldn’t normally incur, but do so to minimize the loss and keep the business moving. For example:
- Renting equipment to speed up reopening
- Paying overtime to workers who are helping with recovery
- Temporary website hosting if your primary server is down
One small business I worked with used their extra expense coverage to launch an online store while their physical shop was under repair. That online revenue helped cushion the blow and they kept it going after reopening.
So yes, this part of the policy is like the Swiss army knife of insurance it covers creative workarounds when you’re scrambling to stay afloat.
What’s Not Covered (Don’t Skip This!)
I’d be doing you a disservice if I didn’t mention what isn’t covered because assuming you’re covered for everything can be a costly mistake.
Typically not covered:
- Property damage (you’ll need commercial property insurance for that)
- Utilities (unless they’re part of a reimbursed extra expense)
- Earthquakes or floods (unless added separately)
- Undocumented income (keep those records clean!)
- Government-mandated closures (unless explicitly included many weren’t covered during COVID)
- Pandemics and viruses (again, often excluded unless specifically endorsed)
Always, always, always read the exclusions section. Or better yet ask your insurance rep to walk you through a few “what-if” scenarios so you know exactly what to expect.
Why It’s More Important Than You Think
If you’ve never thought much about this kind of insurance, you’re not alone. I used to be the same way. When I helped my cousin start a small boutique in Denver, we were focused on inventory, branding, and rent. Insurance felt like an afterthought until the unexpected happened.
A massive snowstorm shut down the area for two weeks. No customers, no sales. The rent didn’t take a snow day, though.
That’s when I realized: Business interruption isn’t rare it’s inevitable. Whether it’s a natural disaster, a power outage, or a burst pipe, most businesses will face some form of disruption at some point.
In fact, according to FEMA, 25% of businesses don’t reopen after a major disaster. And in the wake of COVID-19, we all got a brutal reminder of how fragile operations can be when they’re interrupted.
What Triggers a Business Interruption Claim?
This is where things get a little technical but stick with me, because it matters.
Your policy will outline what specific “covered perils” can trigger a claim. Most common triggers include:
- Fire and smoke damage
- Storms or wind damage
- Theft or vandalism
- Equipment breakdown
- Natural disasters (depending on your policy)
However, pandemics, virus outbreaks, or government shutdowns are typically excluded unless explicitly written into the policy. This caught a lot of businesses off guard during the pandemic when they realized they weren’t covered for government-mandated closures.
So when you shop for business interruption coverage, read the fine print. Ask questions like:
- What events are covered and excluded?
- Is there a waiting period before coverage kicks in?
- How long will coverage last? (Known as the “restoration period”)
Real-World Example: The Bakery That Bounced Back
Let me share a real story that stuck with me.
In 2021, a popular bakery in Portland let’s call it “Maple & Crust” suffered a small kitchen fire. Thankfully, no one was hurt, but the damage meant they had to close for nearly two months for repairs and inspections.
They had invested in business interruption insurance a year prior. Their policy covered the lost revenue, rent, and payroll. Not only did they keep their team on board, but they also used part of the extra expense coverage to launch an online delivery service during the downtime. By the time they reopened, they had expanded their customer base beyond the neighborhood.
That’s the power of preparation.
How Much Does Business Interruption Insurance Cost?
Cost varies depending on factors like:
- Type of business and industry
- Business location
- Annual revenue
- Risk exposure (e.g., fire-prone area vs. safe suburb)
- Desired coverage limits
On average, most small businesses might pay $500 to $1,500 annually for this coverage. It’s often bundled with commercial property insurance or as part of a Business Owner’s Policy (BOP) which can be more affordable than buying it separately.
Yes, it’s an extra cost. But think of it like a seatbelt. You hope you’ll never need it, but if you ever do it can save your business.
What to Look for When Buying a Business Interruption Policy
Let’s be honest buying insurance isn’t exactly exciting. It’s one of those grown-up tasks that feels more like a chore than a triumph. But when you’re running a business, it’s not just about checking a box. The right business interruption policy can be the thing that saves your business from total collapse when life throws a wrench in your operations.
That said, not all policies are created equal. And in my experience helping other entrepreneurs and reviewing policies for my own ventures, I’ve picked up a few things to keep in mind before signing on the dotted line.
This part is about asking the right questions and watching for the right details, so you don’t end up surprised later.
1. Understand the Triggers: What Counts as an Interruption?
Start here. Every policy will list specific events that “trigger” the coverage meaning, these are the situations where your policy will actually kick in and pay out.
Ask your agent or insurer:
- Does this cover natural disasters like wildfires or hurricanes?
- What about utility failures, vandalism, or cyberattacks?
- Will it cover closures due to nearby construction or government orders?
You want to be crystal clear on what scenarios are included and, equally important, what’s excluded.
For example, one business owner I knew assumed their coverage included flood damage because their building was in a low-risk zone. Turns out it didn’t, and a burst pipe left them out of commission (and out of luck) for over a month. The lesson? Never assume. Always verify.
2. Check the Waiting Period
Here’s something most people don’t think about until it’s too late: business interruption policies usually have a waiting period a set amount of time you have to wait after the incident before your coverage kicks in.
This could be 24 hours, 72 hours, or even a week, depending on your provider.
It may not sound like much, but think about how much you could lose in three or four days if you can’t operate. Rent doesn’t pause, and your staff still needs to get paid.
When reviewing a policy, ask:
- How long is the waiting period?
- Does it start from the moment of damage or from the time I file a claim?
- Is there an option to reduce it for an additional premium?
Sometimes spending a little more to shorten that waiting window is absolutely worth it.
3. Know Your Coverage Limit and Restoration Period
Next up: how much coverage you’re getting and for how long.
The coverage limit is the maximum amount the insurance company will pay out. If your business needs $100,000 to stay afloat but your policy only covers $50,000, you’re on the hook for the rest.
The restoration period, on the other hand, is how long the policy will cover your lost income while you’re recovering. This typically ranges from 30 days to 12 months or longer. But here’s a little known fact: even if you’re not back to 100%, coverage could end once the insurer deems that “reasonable restoration” should be complete.
Translation? You could still be struggling to get back to full speed but stop receiving compensation.
Pro tip: Ask for an option to extend the restoration period or purchase an endorsement if you’re in a business that takes longer to bounce back like manufacturing or medical services.
4. Look at Extra Expense and Contingent Coverage Options
Most standard policies will cover lost income and fixed costs. But the really solid ones go further by including extra expense coverage.
That’s what helps you:
- Rent temporary equipment
- Launch a pop-up store or mobile location
- Cover emergency advertising to let customers know you’re still around
Also worth asking about: contingent business interruption insurance. This kicks in when your suppliers, partners, or distributors go down and your business suffers as a result.
Say you run a smoothie bar that relies on a produce distributor. If their warehouse floods and you can’t get your ingredients for weeks, contingent coverage could help replace that lost income. It’s especially important if your business relies heavily on a third party for products or materials.
5. Ask How Claims Are Calculated
This one’s big and often overlooked.
Insurance companies will look at your historical financial data to calculate how much income you’ve lost during a shutdown. If your records are spotty or outdated, that could mean a smaller payout.
I always tell fellow business owners: Treat your bookkeeping like your business depends on it because it does.
When reviewing a policy, clarify:
- What documentation is required to prove loss?
- Will seasonal trends or growth projections be considered?
- How do they handle new businesses with limited financial history?
It helps to have a solid relationship with your accountant too. Trust me during a crisis, having clean, up-to-date records is a godsend.
6. Make Sure It’s Tailored to Your Business
Last but not least, avoid cookie-cutter policies. A café’s risks are different from a software firm’s. A boutique might bounce back in a week, but a manufacturing plant might need months.
Work with someone who understands your industry. That might mean:
- A local agent who knows your area and its risks
- A commercial insurance specialist who’s helped similar businesses
- Or doing your own research and comparing quotes from reputable providers
Don’t just go with the cheapest option. Go with the one that fits your business like a glove.
Buying business interruption insurance shouldn’t be something you rush through or shrug off. It’s not just paperwork it’s your safety net. It’s the plan B you hope you never need, but will be incredibly thankful for if disaster strikes.
Take the time to sit down with someone you trust. Ask “dumb” questions. Go through worst-case scenarios. The more you understand now, the less stressed you’ll be later if things go sideways.
Peace of mind is worth every penny. And when you’ve built something with your own two hands, protecting it isn’t just smart it’s essential.
A Hypothetical Scenario: The Freelance Designer
You might think this insurance is only for brick-and-mortar businesses but what about digital or remote ones?
Imagine you’re a freelance designer working from home. A major power surge fries your laptop and backup drive. You lose access to client files, can’t deliver work, and need to rent a coworking space plus buy a new laptop.
Now, a standard business interruption policy might not cover you unless you have home-based business insurance with specific endorsements. The takeaway? Always customize your coverage to match your actual risks.
Final Thoughts: Is It Worth It?
If you’re still on the fence, ask yourself this: Could your business survive 1-3 months without revenue?
If the answer is no (and let’s be honest, for most small businesses, it’s no), then business interruption insurance isn’t a luxury it’s a lifeline.
It’s not about being paranoid. It’s about being smart. You’re not just protecting your income; you’re protecting your employees, your customers, your reputation, and your future.
Take Action Today
- Review your current business insurance. Do you already have this coverage? If not, what would it cost to add it?
- Talk to your agent. Have a frank conversation about risks and what-if scenarios.
- Update your emergency plan. Insurance is just one piece of the puzzle make sure you’re ready for disruptions in other ways too.
Disruption doesn’t knock before it enters. But when it does, business interruption insurance could be the safety net that catches you.
Stay safe, stay covered, and keep building.